Basic Theories
A little explanation of Photoelectric Effect ( in brief)
Before we go deep inside the details of Quantum Mechanics, firstly we have to understand the basic theories which are related to it and Photoelectric Theory is one such theory......Exited??? So, let's get started..........
By hearing the word ‘Photoelectric’ it seems quite
interesting, isn’t it? Yeah, thats true its pretty interesting and the history
of its is also amazing. We all know that Einstein got Nobel prize. But do you
know for which theory he got the same? Its actually for the Photoelectric
effect!!!
According to the Bohr’s model, its necessary to
provide electrons with energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation in order
for them to get to orbitals with higher energy. However, if an electron absorbs
a wave of high frequency, sometimes this energy is sufficient to abandon the
atom entirely. This phenomenon, when the electrons are released from the shell
of atom is called the photoelectric effect.
It has been observed that there must
be a minimum energy needed for electrons to escape from a particular metal
surface and is called work function ‘W’ for that metal. The work function can
be expressed in terms of frequency as,
W=hVo…………..(1)
Where, h is the Planck’s constant and Vo is the threshold
frequency (minimum frequency for photoelectric effect).
According to Einstein the
Photoelectric effect should obey the equation,
hV=KEmax
+W………….(2)
From the above expression,
KEmax=hV-hVo
KEmax=h(V-Vo)…………..(3)
While Young’s experiment convincingly
demonstrates the wave nature of light, the photoelectric effect sees light as a
stream of particles. Therefore, electromagnetic radiation has both wave and
particle nature.
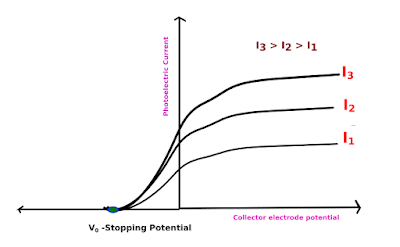
Stoping Potential:-
Photoelectrons are emitted from a metal, when
illuminated with light, above the threshold frequency of the metal, with a
range of KE’s. The stopping potential is the voltage between the metal surface
and a cathode, placed close to the surface, in a vacuum, which just stops them from
producing a current. We can then assume that the max KE of the photoelectrons,
KE(max) =
eV(s)…….(4)
where,V(s) is the stopping potential.
Einstein theorized that photons transfer an energy
equal to E(p) = hf, and that the minimum energy required for a photon to
penetrate the surface is a constant, called the ‘work function’ of the metal,
W.
Cheers!!! See you Again......👍👍👍
Don't Forget to check our other posts too.........
Subscribe to the Blog and follow my social handles for latest updates........
You can directly talk with me on Instagram
To meet more physics Enthusiasts please join our Facebook Page
To meet more physics Enthusiasts please join our Facebook Page
Also for latest updates of my posts join me on Twitter
Founder and Writer of The Dynamic Frequency












0 Comments